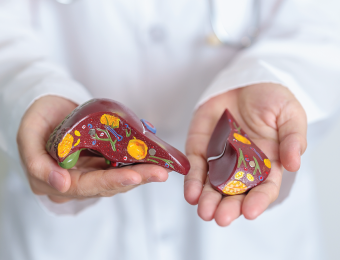
Innovation in Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Fat Accumulation
"Liver fat accumulation" is a common cause of liver disease nowadays, which can progress to conditions like fatty liver and liver cancer. It also increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and liver failure. In this article, we will discuss methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing liver fat accumulation often relies on clinical observation of the Metabolic syndrome, characterized by obesity, diabetes, high blood lipid levels, low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension. It's crucial to rule out other causes of liver fat accumulation.
However, patients with liver fat accumulation may not exhibit all characteristics of Metabolic syndrome when they visit the doctor. Alcohol consumption is a common cause of liver fat accumulation. Therefore, it's essential to determine if the patient consumes alcohol or if the amount consumed is below the threshold for liver disease. The threshold for alcohol consumption that can lead to liver disease is approximately 20 grams per day for women or 40 grams per day for men. A simple guideline is to consume less than 14 units of alcohol per week to prevent liver disease. For individuals with other liver diseases, approximately 1 unit, equivalent to one can of beer, one glass of wine, or one shot of whiskey, per day is considered safe.
In additional laboratory testing to diagnose liver fat accumulation, abdominal ultrasound is a convenient method. Ultrasound can detect a liver that appears brighter than normal, but it lacks sensitivity and may only show signs of fatty liver when fat accumulation exceeds 30%. For faster diagnosis, computed tomography (CT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is utilized, revealing a darker liver compared to normal.
These imaging techniques can detect liver fat accumulation starting from 5-10%. Newer MRI models can also quantify liver fat content indirectly. Currently, Fibroscan devices are used to assess liver stiffness and steatosis. The latest Fibroscan models can measure liver fat content directly.
After diagnosing liver fat accumulation, the underlying causes must be investigated. These causes may include chronic viral infections, such as hepatitis C, or metabolic disorders like Wilson's disease.
In some cases, patients may require a liver biopsy for diagnosis, particularly when the cause cannot be determined otherwise or when the patient is unresponsive to treatment. Treatment for fatty liver disease focuses primarily on weight reduction, especially in overweight individuals. Weight loss should be achieved through dietary control and exercise. In terms of dietary control, reducing evening meal portions and minimizing intake of carbohydrates, sugars, and fatty foods is essential. A healthy diet for patients with fatty liver disease should include high-fiber foods such as vegetables and good sources of protein like legumes. Animal protein should preferably be lean meat or seafood rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as tuna, salmon, and sardines. Cooking methods should involve boiling or steaming, and if frying is necessary, coconut oil is recommended. Opt for fruits that are not overly sweet, such as guava and apples, as they are rich in vitamin C.
Regarding coffee consumption, studies have found it to be beneficial due to its antioxidant properties. However, it's advisable to drink black coffee without milk and sugar. Patients with fatty liver disease should avoid alcohol consumption, as even moderate intake increases the risk of liver cancer. Exercise is crucial, with a recommended duration of 30-60 minutes per day. Rapid weight loss, particularly through fasting, should be avoided, as it can lead to severe liver inflammation. In practical terms, weight loss should not exceed 1.6 kilograms per week.
Key medications for treating fatty liver disease include insulin-sensitizing agents for those with diabetes or insulin resistance, such as Metformin. For individuals with high cholesterol levels, medications to lower blood lipids may be prescribed. In cases of ongoing liver inflammation, physicians may consider prescribing antioxidants to reduce inflammation. Patients with fatty liver disease should receive continuous medical care to monitor treatment response, disease progression, and the development of other conditions associated with metabolic syndrome.
25 Dec, 2023

Neungruethai Phirom, M.D.
Specialties Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology

Jittpat Thanomteeranunt, M.D.
Specialties Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology

Nontapat Kantathavorn, M.D.
Specialties Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology

Pattama Kiatpapan, M.D.
Specialties Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology
 EN
EN
 TH
TH CN
CN