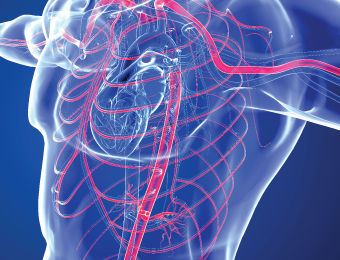
CT Coronary artery Calcium Scoring
Calcium or limestone in the heart can adhere to the walls of the arteries, heart valves, or the heart's outer lining. What is concerning is the limestone that adheres to the walls of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscles. This condition arises from the deterioration of the red blood vessels and can occur many years before the symptoms of heart disease manifest. Studies have shown that the amount of calcium can predict the likelihood of developing coronary artery disease, beyond other risk factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or smoking. The presence of calcium deposits in the arteries increases the risk of sudden cardiac muscle death from acute arterial blockages.
Who should undergo CT Coronary artery Calcium Scoring?
The American Heart Association recommends that the following individuals should undergo coronary artery calcium screening:
- General patients aged 45 and older.
- Patients with intermediate risk of heart disease.
- Patients with diabetes or chronic kidney disease.
According to recommendations from the American Diabetes Association, patients with diabetes, older patients, and those with chronic kidney disease who cannot undergo standard stress testing should consider coronary artery calcium screening as a good standard for heart examination.
Getting a CT coronary artery calcium scoring test offers several advantages:
Undergoing a CT coronary artery calcium scoring test provides valuable information for predicting cardiovascular risk, guiding preventive strategies, and facilitating early intervention, ultimately leading to better management of heart disease and improved patient outcomes.
Why identify those at risk?
Because preventing this disease is something everyone can do, regardless of their level of risk. Actions like quitting smoking, regular exercise, reducing fat intake, adequate rest, and stress management are beneficial for everyone, especially those with high blood pressure and diabetes. By controlling blood pressure to below 140/90 mmHg and LDL cholesterol below 130 mg/dL, individuals can proactively manage their health.
CT Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring is a rapid and non-invasive method for assessing calcium levels in the coronary arteries. Using advanced 128-slice CT scanners, this technique provides clear images without the need for contrast agents, allowing precise measurement of calcified plaque accumulation. Even small amounts of calcification can indicate the early stages of coronary artery disease in otherwise healthy individuals. A calcium score of zero is typical for newborns with normal arteries, but as individuals age, some calcification may be present, ideally not exceeding 200-400. Scores over 400 indicate a significantly elevated risk.
25 Dec, 2023
 EN
EN
 TH
TH CN
CN