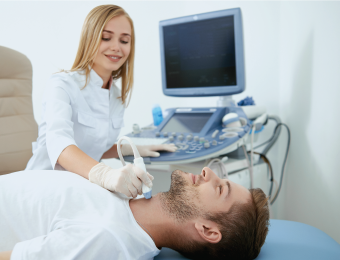
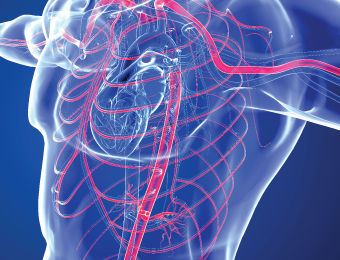
Are you at risk of heart failure?
Heart and blood vessel disease can stem from high blood cholesterol levels or abnormal levels of triglycerides, or both. High cholesterol levels can lead to the hardening, narrowing, and blockage of blood vessels in the future, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease.
High blood cholesterol can result from several factors, such as:
External factors:
- Obesity or being overweight
- Lack of regular physical activity
- Regular alcohol consumption or smoking
- Consuming foods high in cholesterol
- Genetics
- Thyroid disorders, diabetes, kidney disease, or the use of certain medications
This genetic disorder manifests in two forms:
-
Heterozygous FH (Familial Hypercholesterolemia): Inherited from one parent, individuals typically exhibit total cholesterol levels ranging from 350 to 500 milligrams per deciliter.
-
Homozygous FH: Inherited from both parents, this form results in more severe symptoms, with total cholesterol levels typically ranging from 500 to 1,000 milligrams per deciliter. Individuals with this form face a significantly higher risk of developing sudden heart attacks and premature death.
Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches:
When there's suspicion of risk, combined with abnormal blood cholesterol levels despite medication, genetic testing can identify familial predispositions before specific treatments are administered. Consistent medication adherence and following dietary recommendations as advised by healthcare providers can effectively mitigate the risk of sudden heart attacks and strokes in the future.
25 Dec, 2023
 EN
EN
 TH
TH CN
CN